A look at their key features and operation
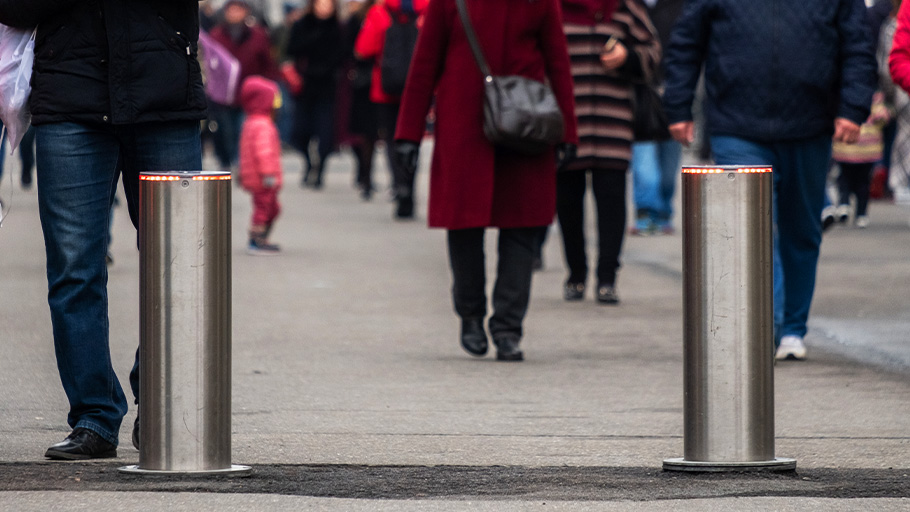

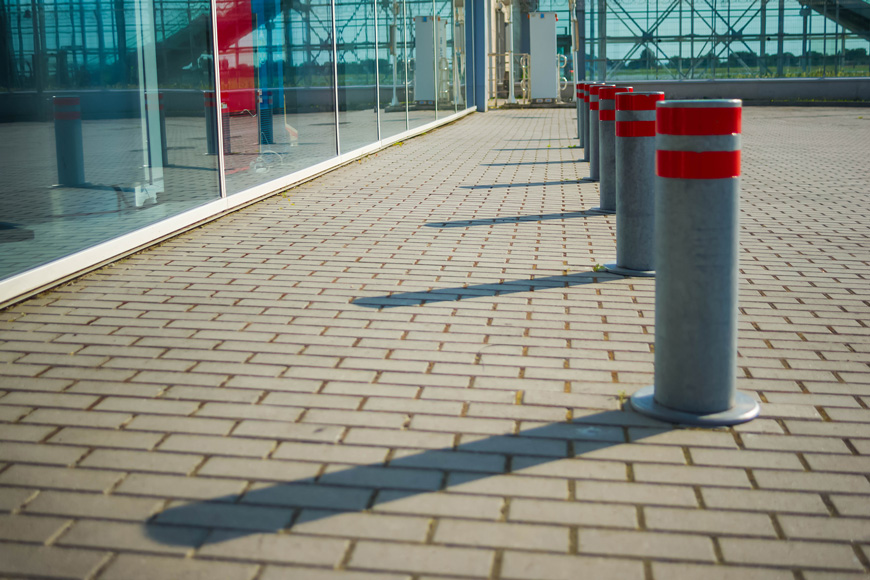
The use of automatic bollards as a dynamic means of controlling vehicle access to restricted areas has increased in popularity as the technology that drives them becomes more sophisticated and reliable. These bollards can be raised or lowered automatically to control traffic flow as needed. They are used in a variety of locations and scenarios where static bollards aren’t suitable.
What Are Automatic Retractable Bollards?
Retractable bollards are bollards that can be positioned fully extended, or fully retracted below ground. Automatic retractable bollards function the same way, but instead of being manually repositioned, they rely on power systems to automatically raise and lower them.
How Are Automatic Bollards Used?
Like retractable bollards, automatic bollards are primarily seen in urban areas where access requirements vary. For example, certain areas in city centers might be busy during rush hour but blocked off to all but pedestrian traffic during weekends or events. Bus priority lanes can also be blocked off to all but the specified users, decreasing unauthorized use.
Another common use is anywhere a barrier gate might be used. While lift gates are a visual deterrent, automatic bollards can replace a lift gate, such as at a parking garage, rail crossing, or toll booth, to perform the same function but with added security.
Benefits of Automatic Bollards
Since automatic retractable bollards can be raised or lowered as needed, they can regulate traffic flow and control the number and types of vehicles that can enter specific roads, laneways, or parking areas. They help reduce traffic congestion and improve safety, particularly in densely populated areas where cities need to manage not only vehicle traffic, but foot traffic and cyclists as well.
This also allows buses and other forms of public transportation to continue to access areas that would otherwise be blocked off with non-retractable bollards. While manually retractable bollards are an option, they require much more time to operate than automatic operation. For areas where the access requirements change frequently, automatic bollards are the best option.
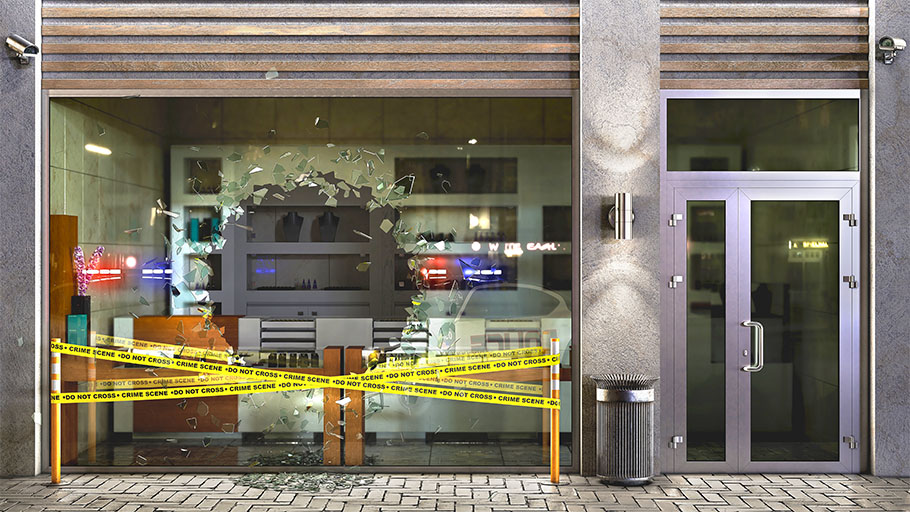
Traditional bollards primarily serve to increase safety. They provide pedestrians with peace of mind, knowing that there is some sort of physical barrier between them and passing vehicles, but they can also effectively protect infrastructure, particularly in high-security areas such airports, military bases, and government buildings. Automatic retractable bollards have the added advantage of being effective at bolstering existing security measures. Installing them in front of an access gate provides an additional layer of security and can reduce, or even eliminate the potential for vehicles to impact gates or guard booths. In cases where a simple lift gate has been used, automatic bollards can be used instead to provide a much more robust solution.
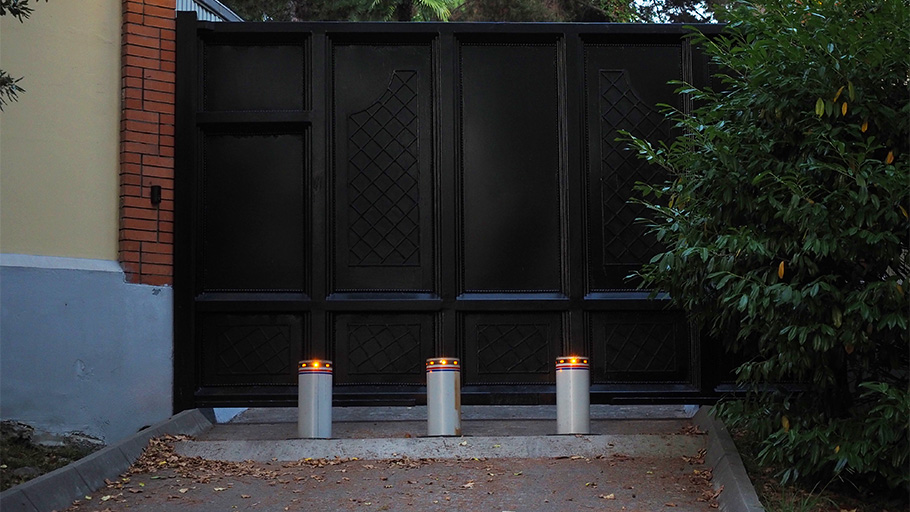

How Do Automatic Bollards Work?
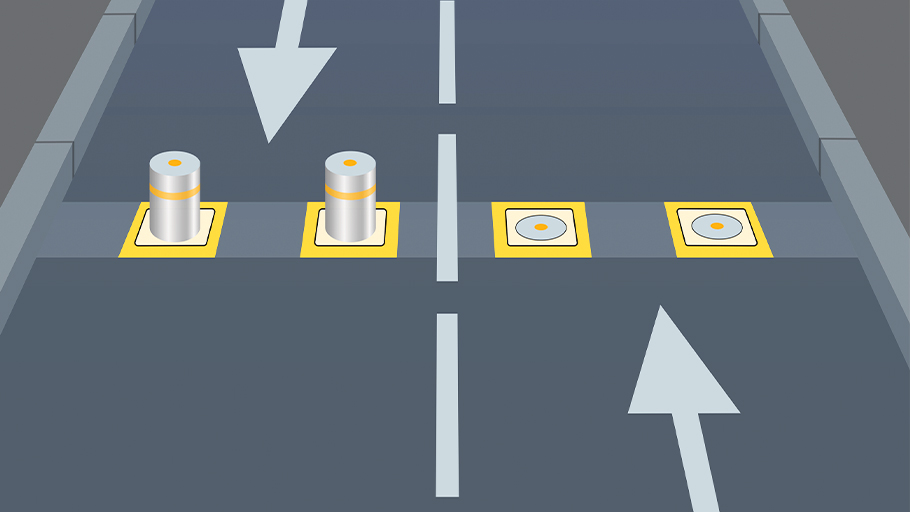
Unlike static bollards, automatic bollards require a mechanism to raise and lower them as needed. The installation of retractable bollards also requires more space, as the entire visible portion of the bollard needs to be able to fit underground when lowered. In operation, a remote signal is sent to the bollard’s control system that tells the logic system which action to take. This signal can be sent using a variety of methods, such as radio transmitters, key cards, intercoms, advanced plate recognition systems, or simple button controllers. The bollard is then either driven up or down, but there are several different power systems available to make this happen. Two of the most common are hydraulic and pneumatic systems, though electric and battery-powered systems also exist.
Hydraulic Bollards
Hydraulic bollards systems use hydraulic fluid to drive the cylinder. To raise the bollard, fluid is pumped into the cylinder. When the bollard is to be lowered, the fluid is released, allowing the bollard to lower back into the ground. This method of driving automatic bollards provides the most force, which makes it ideal for moving the heaviest of steel bollards. It also allows for much more robust stopping capacity. They are often more durable than pneumatic systems, but they are significantly more expensive, both in initial cost, and regular maintenance. They have more moving parts, and unlike air, the substance that drives the system is contained in a closed loop system and needs to be changed at regular intervals.
Pneumatic Bollards
Pneumatic bollards use compressed air to control the column using an external pneumatic power system. When the bollard is to be raised, air is forced into the cylinder causing it to rise. When the bollard is to be lowered, the air is slowly released to ensure the bollard is recessed smoothly. Pneumatic systems are the most cost-effective option. They have fewer moving parts than a hydraulic system and require less maintenance. Their initial cost is also much lower than a hydraulic system and, if noise is a consideration, pneumatic systems can be much quieter. With significantly less operating force, they can’t lift nearly as much weight as hydraulic systems, limiting their use in high-security systems.
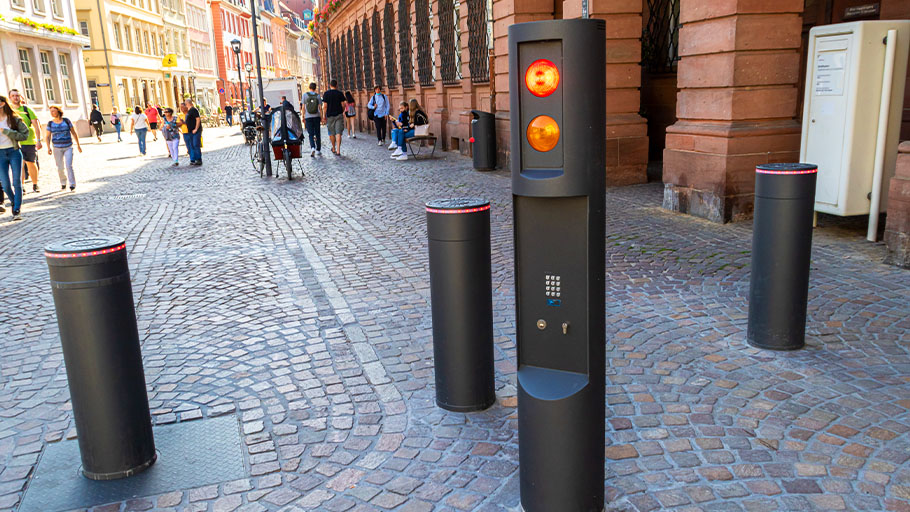

Automatic Bollard Considerations
While automatic bollards can offer a wide range of benefits over static bollards and manually retractable bollards, there are some things to consider:
- Like all mechanical devices, automatic bollards can experience malfunctions such as failure to fully retract or extend. A bollard that isn’t sitting flush with the ground can also create a potential tripping hazard.
- Automatic bollards require regular maintenance to ensure longevity and proper operation.
- Unauthorized or accidental operation: As most methods of operation utilize some form of remote control, it’s important that those controls are secure and only accessible to authorized operators. It’s also important that operators have a clear view of the bollards when they are raising or lowering them, to avoid accidentally obstructing moving vehicles or pedestrians.
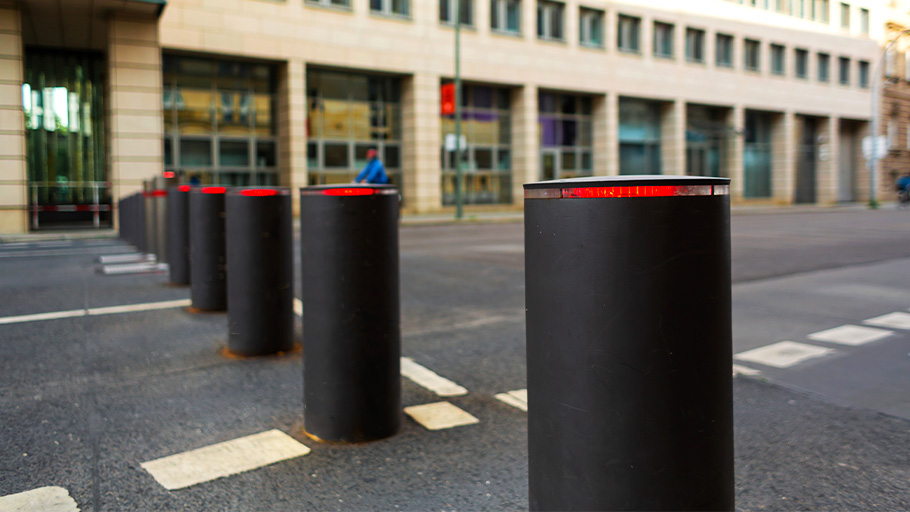

Automatic retractable bollards have been a practical solution for traffic management, pedestrian safety, and security for decades. While these are often seen in European cities such as London, Paris, and Amsterdam, they are also popular in Asia, with many cities in Japan and China implementing them to regulate the flow of vehicles and pedestrians in shared public spaces. They have proven effective at preventing unauthorized vehicle access, controlling traffic during peak times, and improving the safety of pedestrians and cyclists alike.
Although automatic bollards are less widely used in North America than in other regions of the world, they are becoming more common in urban areas to control access to pedestrian areas and to enhance security. As many cities in North America adopt the concept of shared streets, automatic bollards will have an important role to play in creating safer environments for people to walk, cycle, and socialize.