Site planning and installation for bike racks, lockups, and lockers
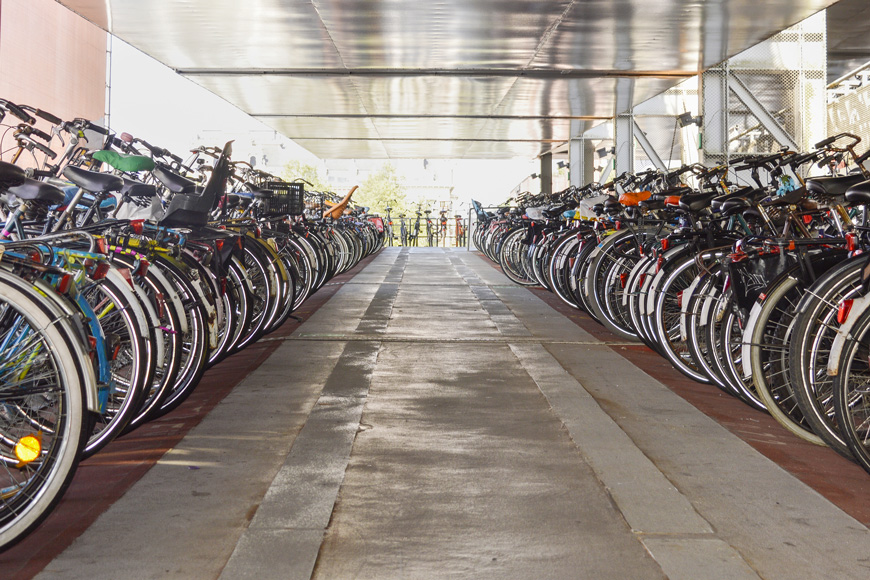

As society shifts towards sustainable living, a cleaner alternative to automobile commuting is gaining traction. Cycling offers benefits that surpass driving on many levels—an economically and environmentally sound option that helps people to fulfill health and fitness goals.
While cycling proves to be an excellent method of transportation, an important question remains: Where can a bike be conveniently stored once the cyclist reaches their destination?
Bike parking becomes essential in the proper operation of any bicycle program, especially in high-density areas. Without the support and convenience of bike parking at a local level, cyclists can quickly feel discouraged in their choice of transportation. A cyclist must be able to find a place to park or store their bike efficiently, effectively, and securely. This concerns cyclists who bike to work or for leisure, including those who live in apartment complexes, college dormitories, or other residencies where the question of where to store a bike at home is uncertain.
Bike parking categories
Bike parking can be divided into three main categories:
- Bike racks or bike bollards (short-term)
- Bike lockers (long-term)
- Bike lockups (long-term)
Before delving into the specifics of each type, the duration of bike parking should be considered. This affects the type of bike parking required and helps the cyclist to determine whether a bike rack or bike locker would be more suitable.
Short-term bike parking
Short-term bike parking is out in the open, unsheltered and unenclosed. It generally provides parking for less than two hours and is typically in the form of a bike rack. The primary advantage of short-term bicycle parking is high convenience as it is often located in the most central, high-traffic areas. There is also some level of security from theft—however, since bike racks are accessible to the public in an open space, there is never a guarantee.
Long-term bike parking
Long-term bike parking is sheltered with added protection and enclosure, and bikes may be stored for over two hours. Long-term bike parking comes in the form of bike lockers and lockups, which includes bike shelters, bike rooms, and bike parking stations. The advantage of long-term parking is that it has a high level of protection against bike theft as it offers an enclosed space. Unauthorized access is largely eliminated, and cyclists can also leave their cycling accessories attached to their bike.
1. Bike rack
A bike rack is one of the easiest and most economical ways to create a short-term parking solution. Outdoor bike racks are common in public or commercial areas, while indoor bike racks are often used for private bike parking.
An effective bike rack meets the following requirements:
- The bike frame, and at least one wheel, is secured with a U-lock.
- The bike is supported upright by its frame in two places.
- The bike wheel does not tip over.
- The bike rack allows for front-in and back-in parking.
- The bike rack does not impede pedestrian traffic and is protected from motor traffic.
- The bike rack is easily accessible from the street.
- A range of bike shapes and sizes can be accommodated.
Types of bike racks
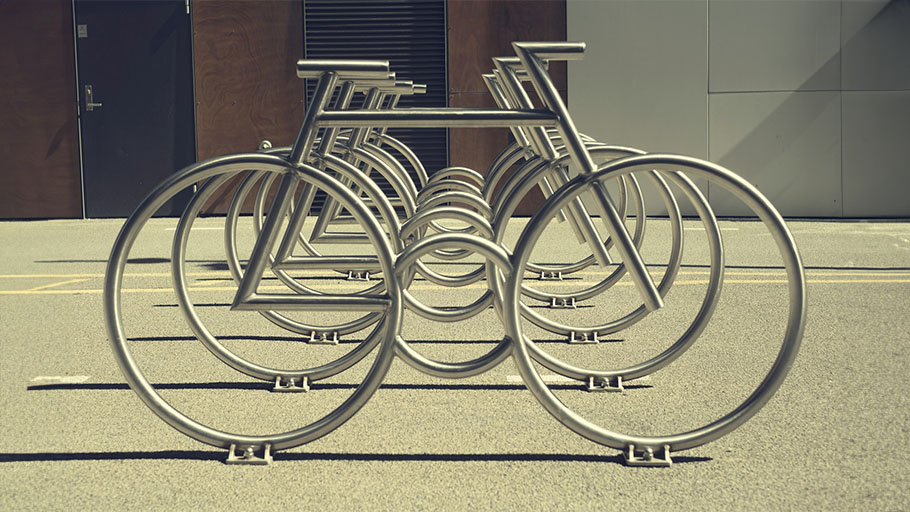
Bike racks come in an array of styles to meet the demands of the cycling community. A few general styles of commercial bike racks exist:

U-rack
A U-rack is in an inverted U-shape with two points of ground contact. It is a reliable bike rack and commonly used in urban areas as it can be placed along sidewalks with minimal space. It allows both the front and back wheels of the bike to be secured.

Wave
A wave bicycle rack comes in an undulating, wave configuration. It offers both an interesting design, as well as functionality, with the ability to secure more bicycles than a U-rack: up to 7.

Grid
A grid bicycle rack is comprised of vertical bars connecting upper and lower metal bars. This allows for bicycles to be parked on both sides of the rack. However, it does not allow for both the wheel and frame of the bicycle to be secured and can lead to increased theft.

Spiral
A spiral bike rack is in spiral formation. Although it has aesthetic appeal, it has functional downsides when it comes to accessibility—the wheel must be lifted in order to park the bike.

Bollard
Bollard bike racks are essentially bollards (short posts) with one or two locking arms that can be used to secure bikes. An advantage to this style is that it can be made removable for a temporary bike rack option.

Double decker
Double-decker bicycle racks are two-tier bicycle racks that can used to increase bicycle storage capacity. However, extra force may be required by the cyclist to maneuver their bicycles onto the higher tier.

Innovative
Innovative bike racks focus on new designs, offering the best of utility and style. Bike rack engineers are typically responsible for these modern designs.

Decorative
Decorative bike racks focus on the decorative and aesthetic elements. They aim to complement the look and style of the surrounding theme or environment.
Bike locks for bike racks
To secure bikes onto bike racks, two types of locks are generally used: U-locks and cable locks. The main differences are in their degree of security and flexibility. For a photographic guide to locking your bike, click here.

U-locks
Bike lock manufacturers typically build locks with enough length to secure both the tire and frame to a bike rack with as little slack as possible. Excess slack should be avoided as thieves can use it to create leverage to break away the bike lock. U-locks are one of the most secure, and most popular, lock types.

Cable locks
Cable and chain-style bike locks are less secure than U-locks. These bicycle locks are typically made from hardened steel, and may feature protective layers such as Kevlar to protect the bike lock from being cut. While these locks offer a bit more flexibility than U-locks, they may be at an increased risk for theft.
Materials
When it comes to material considerations for a bike rack, there are two areas to highlight: the material of the bike rack itself, and the material of the installation surface.
A. Bike rack material
Bike racks can be constructed from various materials as long as the material covers a few important principles: it is durable, water-resistant, and functional.
Popular construction materials for bike racks:
- Stainless steel
- Steel
- Recycled plastic
- Thermoplastic
Construction of bike racks can be completed with a finishing material. This enhances the overall appearance of the bike rack and helps it to endure harsh weather conditions. Examples of finishes include galvanized coating, paint, powder-coating, or IronArmor FrameSafe.
B. Surface material
Bike racks can be installed on different surface materials. Some materials provide a stronger footing, while others may be too soft for surface installation methods.
Concrete
Concrete is the most ideal surface material for bike rack installation. Concrete provides a stable surface for various mounts.
Asphalt or tile
Asphalt and tile is an acceptable surface for bike rack installation but may not offer the same stability as a concrete surface. The thickness of the material, surrounding climate, and what lies below the surface grade will ultimately affect the functionality.
Grass or dirt
Grass or dirt does not provide sufficient grounding for most bike rack systems. A freestanding bike rack may be the only option for these surfaces.
How visible should a bike rack be?
The visibility of the bike rack will determine its usefulness to cyclists, so the need for visibility is very high. Cyclists should be able to quickly identify bike racks when arriving from the street. A highly visible location not only makes it easier for the cyclist, but also curbs theft and vandalism. Areas should also be well lit, and, when possible, place bike racks within view of passerby, retail activity, or windows.
Choosing the best location for a bike rack
Bike racks are the hallmark of short-term parking and convenience is paramount. They should be implemented in areas of high traffic such as building entrances—no further than 50 feet from these entranceways. Bike racks must be visible from adjacent bikeways and allow for fast street access while avoiding locations that have stairs.
It is crucial that bike racks do not impede pedestrian traffic and are safely tucked away from automobile traffic. There should be no protruding bars on the bike rack if installed on a narrow sidewalk. To maximize the use of surrounding infrastructure, consider building a bike rack along buildings that have an existing overhang or a covered walkway—cyclists will appreciate the protection from elements!

Bike rack spacing
From tire-tip to tire-tip, bikes can span up to 7 feet, so site planning must focus on adequate space. Enough swing-room is necessary for bikes to maneuver in and out of parking without obstructing door access, pedestrian right of way, or street furniture.
Many municipalities have detailed setback requirements to avoid crowded or inaccessible bicycle parking. It is recommended that installers check the relevant codes and zoning requirements prior to installation.
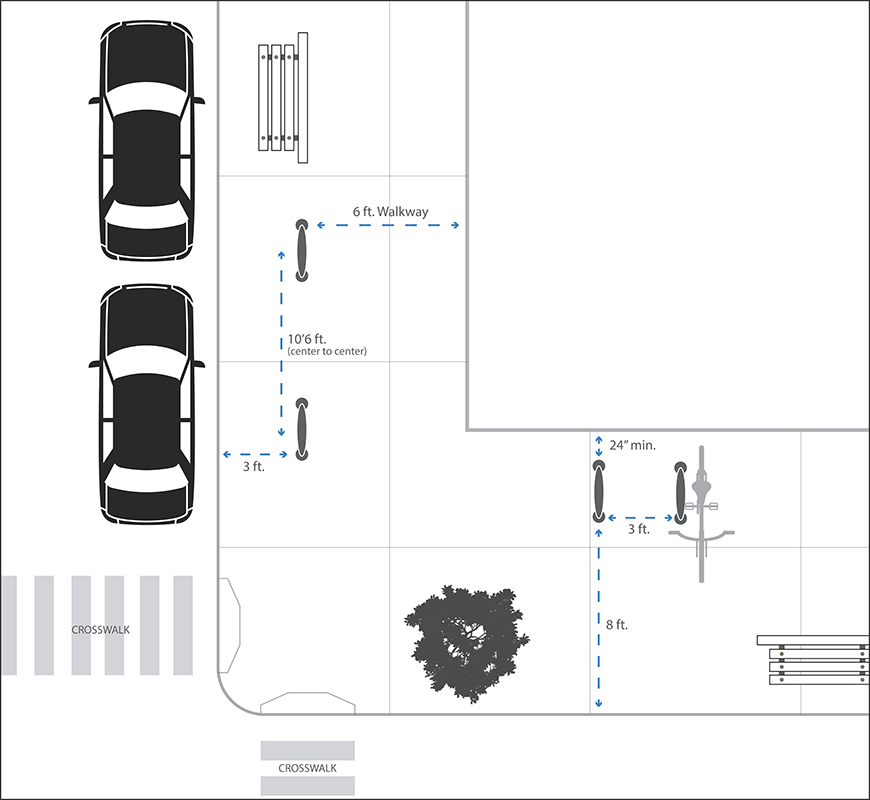
General setback recommendations for bike parking:
Horizontal series
- 24-inch minimum space between a rack and the wall of any building or infrastructure.
- 3-feet minimum space between bike racks.
- 8-feet minimum space between a bike rack and the curb.
Line series
- 6-feet minimum space between a rack and the wall of any building or infrastructure.
- 10-feet 6-inch minimum space between bike racks (center to center).
- 3-feet minimum space from a bike rack and the curb.
Outdoor bike rack installation
Bike rack installation involves racks that are fixed onto the ground, or fixed onto a wall. Most bike racks are a permanent fixture, however, the removable mounting systems of bike bollards allows for the flexibility of a temporary bike rack.
INSTALLATION METHODS FOR BIKE RACKS
In-ground mount
The base of the bike rack is embedded into the ground, and secured with an anchor pin for stability. These mounts are known to offer the highest security.
Surface mount
Flanges that extend from the base of the bike rack are secured into the concrete surface with bolts. For added support, surface mounts can be reinforced with extra hardware when secured into an existing piece of concrete.
Rail mount
Rail mounts are useful for connecting multiple U-racks instead of installing each U-rack individually. This is an economical option that reduces labor costs and the number of holes drilled into the concrete surface.
Wall Mount
Some bike racks are designed to be mounted to the wall. Bolts are used to connect the flanges of the bike rack to a steady wall. This application is best when floor space is minimal and practical for long-term storage.
Removable Mount
A removable mounting system allows the bike rack to become temporarily removable when required. Removable mountings are especially useful in areas with a changing landscape where it may be necessary to remove bike racks to allow temporary access to delivery, maintenance, or emergency vehicles.
2. Bike locker
Bike lockers are stand-alone lockers or boxes designed to hold one or two bicycles per unit. They are an excellent option for long-term bike storage and highly secure. In fact, they are considered to offer the highest standard of security since they not only prevent theft, but also protect against vandalism and weather.
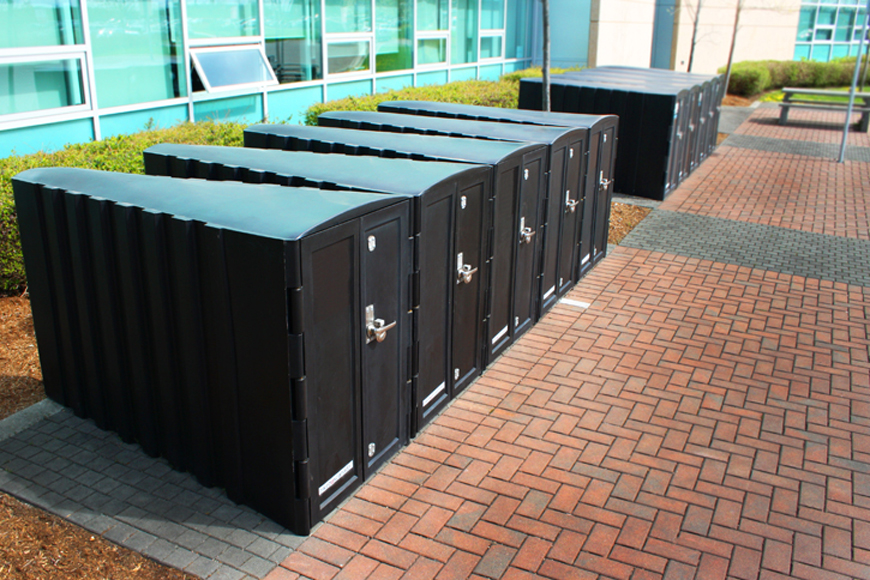

Types of bike lockers
Bike lockers are most often in a rectangular box shape, while some can be in the form of a triangle where the handlebars of the bike face the wider side of the container. Vertical bicycle lockers are also available. It is up to the site planner to decide on a suitable type of bicycle locker based on their evaluation of site space.
Bike locks for bike lockers
After placing the bike into the bike locker, it is secured with a bike lock to prevent theft. The bike lock system depends on whether the bike lockers are rented out ahead of time, or whether they are on a first-come, first-served basis. Generally, those which are rented out for a set duration of time will provide the user with a specific key. Those being used on a casual basis will either be provided with a rental system that dispenses a key/code, or relies on the user to bring their own padlock.
Automated bike storage is also gaining popularity, especially in Europe. These systems often store the bicycles underground with users inserting a microchip card with a code in order to access their bikes.
Materials
Bike lockers are built to protect against weather, vandalism, and theft as they are typically used for outdoor bike storage. Popular materials include steel, reinforced fiberglass, and plastics such as polyethylene.
How visible should a bike locker be?
Bike lockers should be easy to spot for cyclists. Proper signage can go a long way in directing the cyclist to where bike parking is available. As with any theft-prevention device, the bike locker fares better when placed in a well-lit area and within view of passerby. For long-term bicycle storage, the security factor can be increased if the bike locker is placed in clear view of building security or parking lot attendants.

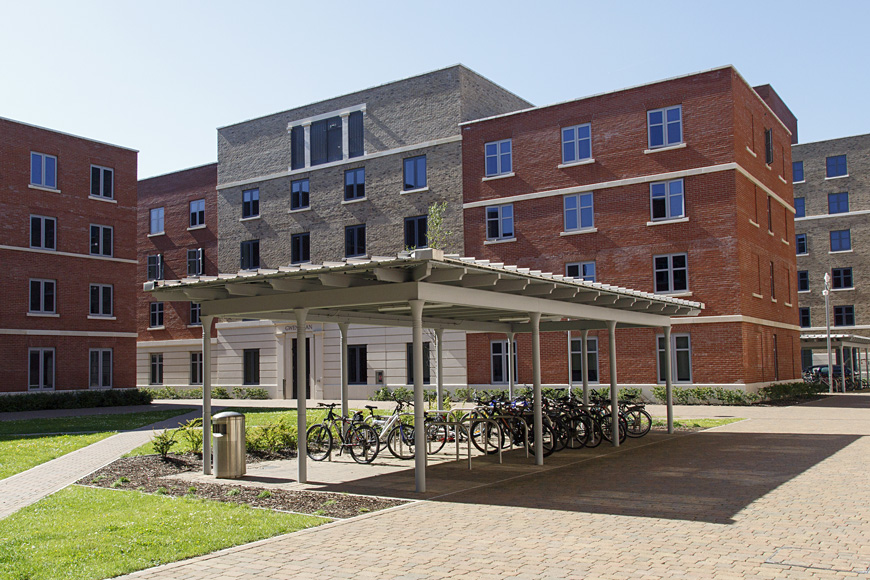
Choosing the best location for a bike locker
Easy access is still paramount when it comes to long-term bike parking. Commercial bike lockers can provide a safe and convenient space for employees to leave their bikes during the workday. Domestic bike lockers are a priority in high-density residential developments. Post-secondary institutions and nearby dormitories are also examples of places with a pressing need for bike lockers.
Site planning for bike lockers
Bike lockers involve careful site planning as more space is required. Spatial considerations will differ depending on whether the site will house a single bike locker or a series of bike lockers.
Single bike locker
Bike locker dimensions will vary by manufacturer. When site planning, allow plenty of room for the smooth flow of users without causing obstruction to pedestrian traffic or nearby street infrastructure.
Series of bike lockers
When installing a series of bike lockers, generous space will be required for cyclists to insert and remove their bikes without blocking the street or colliding into neighboring bike locker users. Several layout options are available to maximize the use of space.
BIKE LOCKER LAYOUTS
Linear
Bike lockers can be arranged next to each other in a row. This is the easiest arrangement, but also takes up the most space.
Triangular
Triangular lockers can be wedged together to form a rectangular box, a space-saving option.
Circular
Bike lockers can be arranged in a circular pattern around a center point, a space-saving option.
Upright
Bike lockers can be placed vertically, where the bike is stored in an upright position. However, this is not common as the process of inserting and removing the bike can be difficult for some users.
3. Bike Lockup
Bike lockups differ from bike lockers in that they do not house one bicycle per unit—they are a shelter that houses multiple bicycles under one roof. Bike lockups provide shelter from the elements, and personal belongings are also safe from theft. Advanced bike parking stations may have staff on hand to look after bikes that have been checked-in, as well as offer bike-related services.
Types of bike lockups

Bike parking stations
These stations vary in complexity and can be as simple as a lockable bike shed to a multi-level building. Bike parking stations may offer additional bike-related services such as bicycle repairs, or amenities such as showers, changing rooms, and washrooms. The priority is to offer secure bicycle parking in high-density traffic areas and convenience through possible added amenities.

Bike rooms
Bike rooms are essentially rooms within a building that have been converted to house bicycles. Bike rooms are often set up when there is no outdoor space to build bike shelters. It provides highly secure, long-term parking for cyclists when there is no other bike parking option nearby.
How visible should a bike lockup be?
It is best to be mindful of safety measures that also increase visibility—keep the area well-lit, clear, and within view of passersby. Installation of surveillance cameras is also recommended. Visibility to cyclists from the street is not quite as pivotal for bike lockups—the emphasis is on security and space, rather than public visibility. Therefore, signage is likely needed to direct first-time users.
Choosing the best location for bike lockups
The best location for bike lockups is an area that allows for generous space—this parking option requires the greatest surface area. Bike lockups should be set up near an exit, avoiding narrow hallways and stairs. If possible, locate the bike lockup near a drainage system so any residual water or mud brought in by the bikes can be cleared.
Site planning for bike lockups
Bike lockups are permanent sites and not mobile. Maximizing floor space is the priority, as well as avoiding clutter and obstruction. The aisle width should be a minimum of 54 inches, allowing one person to walk one bike at a time. If the bike lockup is larger with higher traffic, aisles should be a minimum of 72 inches to accommodate multiple users. If the bike lockup will house bikes with trailers, extra spatial considerations must be made to accommodate the extra capacity.
Bike parking takeaways
Bike parking is essential in any urban community as it offers benefits to cyclists, pedestrians, and motorists alike by reducing obstruction and clutter. Bike parking has varying levels of complexity with options for any space at various price points. The key is to be mindful of site capacity and the surrounding infrastructure and traffic. The integrity of bike parking relies on convenience and security, as well as its ability to enhance, not disrupt, the existing flow of traffic.
Sources
- Broom, Nathan. “Essentials of Bike Parking: Selecting and installing bicycle parking that works“. Association of Pedestrian and Bicycle Professionals. September 2015.
- Federal Highway Administration. “Bicycle Parking and Storage“. US Department of Transportation. July 2006.