Stop accidents in your parking lot and on your site

When setting up a large campus, facility, or parking lot, traffic safety falls to the site planner. Excellent traffic control is important from circulation to signage. Thankfully, most facilities manage slower speeds than those on public roads and highways, which lowers risk. On the other hand, people and cars may be more likely to share the road with pedestrians who may cross erratically through parking lots. In a parking lot, children are more likely to be on the road surface. Additionally, traffic patterns may not be as well established or understood. Facilities can take a page from public roadways and install traffic control devices to keep users safe.
- What is a traffic control device?
- Types of traffic control devices on public roads
- Do public traffic laws apply in parking lots or private spaces?
- Traffic control devices for private facilities
What is a traffic control device?
Traffic control devices direct, guide, and inform drivers by offering visual or tactile indicators. Devices fall into four main categories: signs; signals; road design and marking; and barriers or channelizers.
Types of traffic control devices on public roads
Public roads use a wide selection of traffic control tools which can be adapted to smaller facilities. However, on public roads, driver focus tends to be on signs and signals. In smaller facilities, pavement markings and barriers may take a greater share of the load.
Signs
Road signs provide local information to drivers. Made from reflective material in high-contrast colors, they are highly visible in headlights at night. Signs may use words and symbols to communicate meaning.

Regulatory signs are the most important signs on the road. They declare the accepted legal use of the immediate public roadway.
Intersection control specifies proper behavior when roads meet—signs like stop or yield are essential for preventing conflict and crashes. Speed limit changes are also marked with signs. Traffic direction can be specified, as in one way or no enter signs. Allowable stops or parking spaces are usually marked. Failure to follow regulatory signs often constitutes a moving violation.

Warning signs allow drivers to be aware of driving hazards like animal crossings or twisting paths. They’re installed for maximal safety.
Guiding or informational signs provide route and amenity information to help drivers find their destination. Route and exit information as well as those marking rest stops, gas and food, and tourist attractions all fit into this category.

Traffic signals in red, yellow, and green are ubiquitous items in the traffic control landscape. To the standard three lights may be added lane indicators and other individual lane markings. Flashing lights, either in a traditional signal or hanging alone, are common. However, they can have variable meanings depending on the region and the color. Steadily burning lights are often used as warnings or mark hazards.
Road markings and road construction
Road design offers another vocabulary for communicating with drivers.
Road markings, like lines and arrows, are used to mark correct legal usage of road surfaces. They include stop lines, lane markers, turn lane arrows, and more. Road markings like “sharrows,” showing that bikes and motorized vehicles share the road, notify drivers about unexpected traffic patterns.

Road construction is also involved in traffic control. Rumble strips can mark lanes. When a car drifts over them, they alert through sound and texture that the vehicle is no longer in its lane. Rumble strips are often used in places where drivers might miss a sharp bend in the road, or on long stretches where a driver might fall asleep. Other road construction and environmental design makes certain driving behaviors easier than others. Speed humps and bumps, chicanes, neckdowns, curb extensions, roundabouts and more can encourage proper driver behavior.
Barriers and channelizers
Barriers and channelizers also control traffic, warn against hazards, and mitigate accidents. There are many types.

Traffic delimiters and cones are often placed temporarily to provide warning around hazards or work zones.
Highway barriers, like standard Jersey barriers, help prevent head-on collisions and mark lanes. They can sometimes mitigate or prevent shallow angle accidents by returning a car to the roadway. Highway barriers may be gated or non-gated, either by cushioning an impact of a car but letting it through or by stopping it all together.

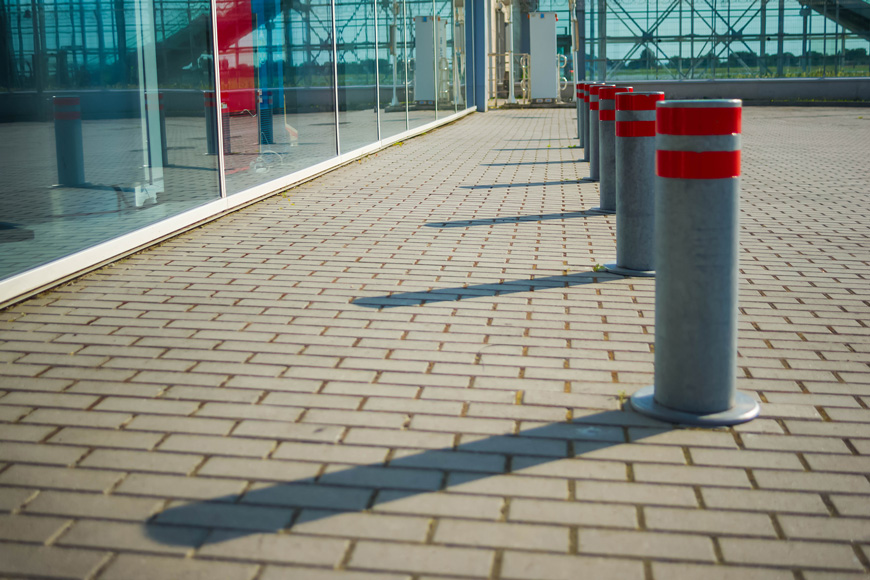
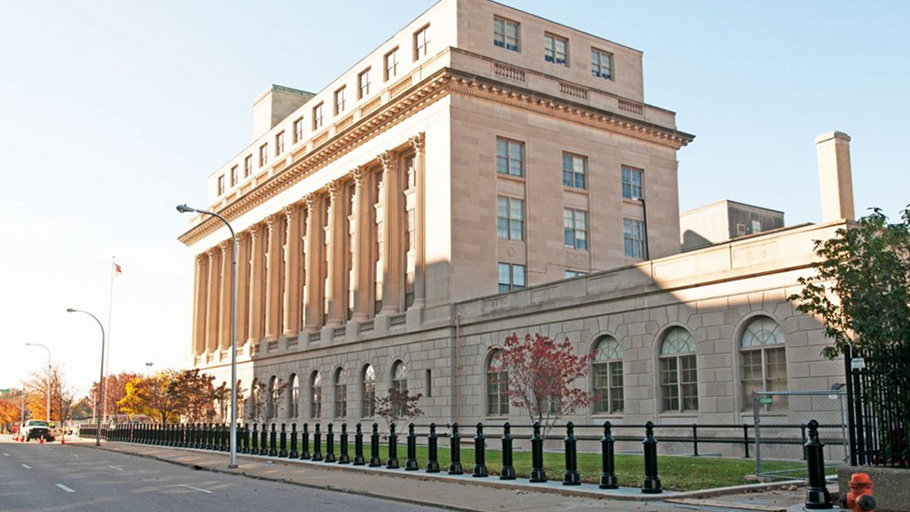
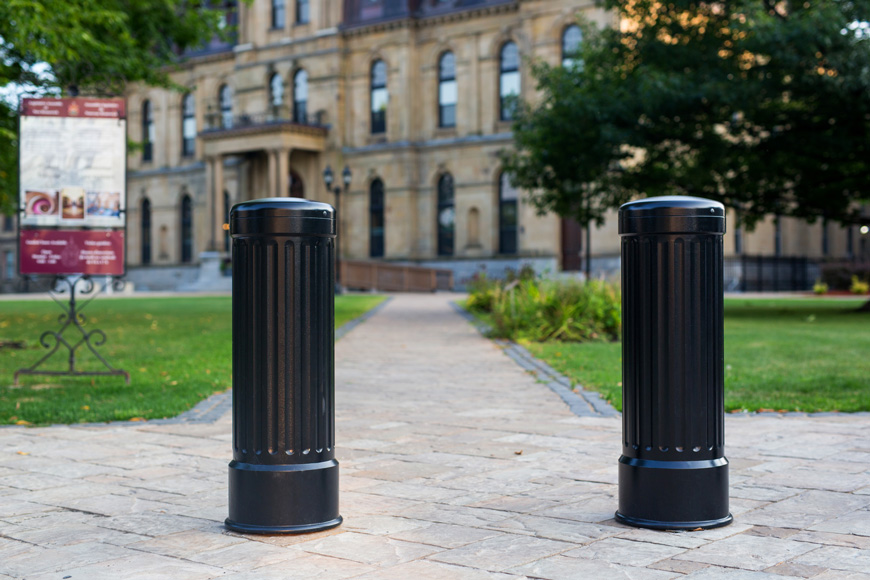
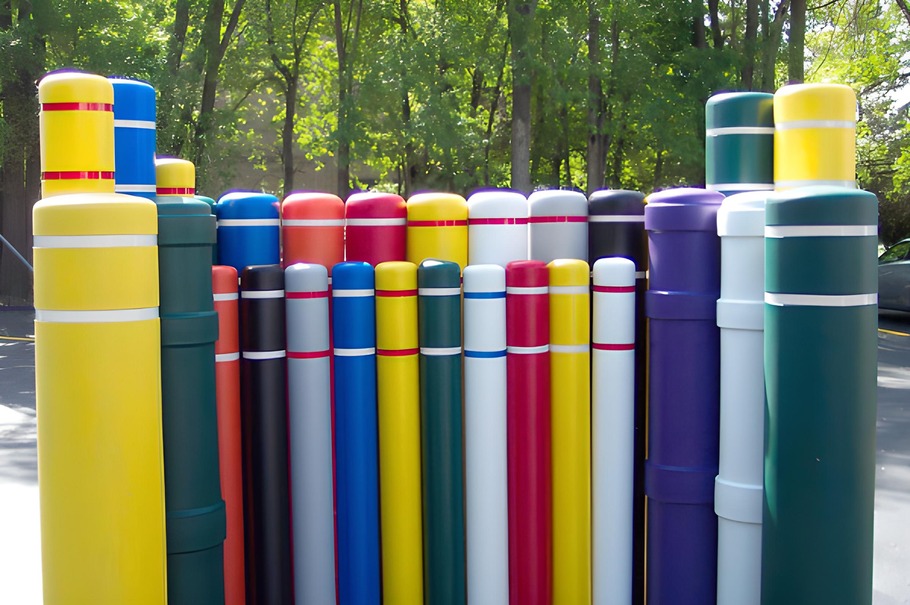
Channelizers and road barriers, whether barrels, curbs, or bollards, are more permanent than traffic delimiters or cones—though some may be removable for multi-access spaces.
Flexible, crash-rated, or security bollards are all used to guide traffic away from certain areas. The crash-rated and security types provide impact protection that is very effective at stopping head on or deep angle crashes.
Do public traffic laws apply in parking lots or private spaces?
In some states and most of Canada, public traffic control markings in private spaces like parking lots must be obeyed. In these jurisdictions, failure to obey a known marker, like a speed limit sign on a campus, can lead to ticketing by local police.
In other jurisdictions, signs on private property do not carry the same possibility for moving violation enforcement. For example, in Ontario, Canada or Washington State, a driver cannot get a ticket for disobeying a marked sign in a private parking lot.
However, even in these jurisdictions, criminal laws do exist that regulate the use of motor vehicles. Drivers may still be charged with things like negligence, reckless endangerment, or vehicular assault or homicide. The private property owner can also ban a driver from returning to their property.
A facilities manager can therefore use standard road markings and signs to communicate the way they’d like their space to be used. Even in jurisdictions where a traffic officer cannot ticket those who disobey, they communicate what is expected enough that refusal may constitute reckless endangerment or negligence.

Traffic control devices for private facilities
Private traffic control often relies heavily on barriers, channelizers, and design. Lights are less common except in very large facilities, due to expense and upkeep.
Humps, bumps, and stops
Speed humps and bumps are a very common form of traffic control in parking lots. They’re also very useful in throughways in residential or commercial complexes, or on large business or educational campuses. Speed bumps provide more aggressive speed control than humps. Parking stops help prevent cars from pulling through empty spots and creating new, possibly unsafe, traffic patterns.
Signs
The most common signs in parking lots are striped warning signs, emblazoned on support pillars and lane dividers. However, speed limit signs can be very useful in conjunction with humps and bumps, to warn people of maximum comfortable speeds. Stop signs are important in large lots and garages where there are intersections that may lead to driver conflict. One-way signs may also be useful in some situations, particularly garages and complexes, although direction of traffic may be marked instead with road markings.
Road markings
Road markings may be very important for through-ways in a residential or commercial complex for traffic control between buildings. Any regular street marking can be used to communicate expected behavior, from sharrows to stop lines. Parking lots also can make use of road markings. Arrows for direction of travel, like those in one-way parking aisles, are often more used in parking lots than one-way signs. Stop lines and turn lanes can also be important with traffic control near the tight corners that can arise in small spaces. Crosswalk and zebra striping create marked pedestrian zones to guide both pedestrians and drivers safely to their cars.
Of course, the most common road marking in a parking lot is the stall marker, which specifies the room allotted for each parked car. Stall markers also may help specify direction of travel, when painted on an angle, as parking lots are often designed with parking orientation that maximizes both space and traffic flow. Markings for accessible spaces also help limit challenges to users in a lot.
Barriers and channelizers
Bollards and jersey barriers are useful in garages. Flexible bollards are useful as parking stops in back-in stalls, as both stop and positioning guide. They are also very handy lane markers on circular ramps that require some flexibility for large trucks to take more than one lane. Crash and security bollards are helpful to prevent pedal error or attack into storefront. Of course, temporary channelizers like cones and delimiters are useful for temporary hazards or construction.
Traffic control and site protection
Creating a private facility with vehicle access means considering the safety of people, assets, utilities, and buildings. There are pedal errors, medical events and driver errors that mean crashes may happen—60 storefront crashes happen every day in the US. Low posted speeds and careful planning through road marking, parking orientation, and environmental may not stop all of these but can mitigate the damage. Protective barriers and bollards can add extra security. As a facilities manager, there is no need to reinvent the wheel: traffic control marking on public roads offers a well-understood vocabulary to communicate desired behavior. Even in states and provinces where moving violations and tickets cannot be handed out on private roads and lots, clear communication means that driver negligence is enforceable. Using traffic control measures can help your users and your property stay safe.
Related Articles:












