Increase driver awareness and pedestrian safety

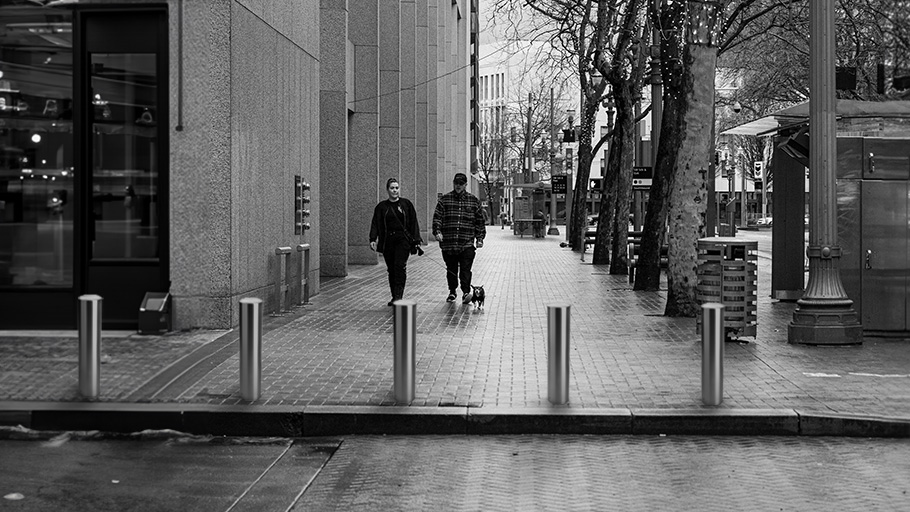
Parking lots can be chaotic. With little to designate safe boundaries between vehicles and pedestrians, hazards can emerge often and without warning. Pedestrians drift between parked cars. Vehicles travel in any direction, backing in and out of parking stalls. Doors open and close. And shopping carts get left in haphazard areas.
Parking lots are also places where people are easily distracted. Many drivers believe parking lots to be safer than streets or highways. This perception of safety can lead to absentmindedness. (John A. Stark offers an excellent resource on the habitual nature of drivers in parking lots in a 2012 report, “Parking Lots: Where Motorists Become Pedestrians.”) And, to exacerbate it all, everyone is in a rush, always. These factors add to a less-than ideal situation.
Despite being so necessary and ubiquitous in our communities, we design parking lots for their utilitarian function—building them for capacity instead of safety and aesthetics. Rarely do they receive the attention given to building interiors and facades. Effective parking lot design takes into account pedestrian safety, as well as efficient vehicle storage—which can be a rarity in many North American cities. In this post, we’ll look at a range of bollard-style barriers to help ensure optimal vehicle and pedestrian flow.
Parking bollards
Bollards identify and protect sensitive parking areas—by helping ensure safe and efficient interactions between vehicles and pedestrians. When spaced properly, bollards create clear, impassable barriers for vehicles while allowing the free flow of pedestrians. For comparison, continuous barriers such as fences and jersey barriers limit pedestrian access to specific entry points—which can be inconvenient, and frustrating, when hurried pedestrians must walk around.
By design, bollards create highly visible barriers to direct traffic and pedestrians
Bollards also protect costly parking infrastructure—such as ticket machines, officer booths and mechanical security gates—or other site furnishings, green spaces, exposed utilities and loading areas that can all benefit from more careful driving.
Choose the right bollard
Bollards provide varying degrees of security and impact resistance depending on their material and mounting type. Visibility and aesthetics, as well as access control, are also factors to consider when designing parking layouts.
Visual protection
By design, bollards create highly visible barriers to direct traffic and pedestrians within a given space.
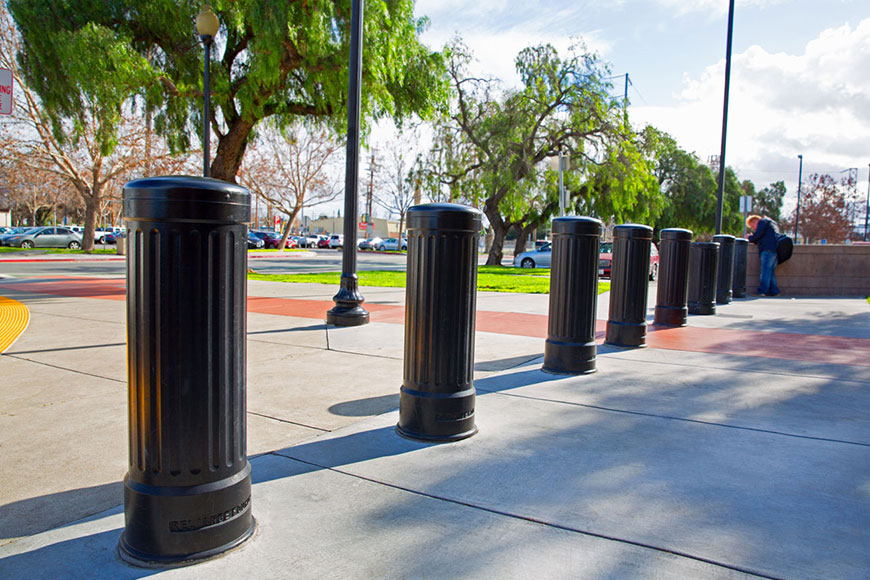
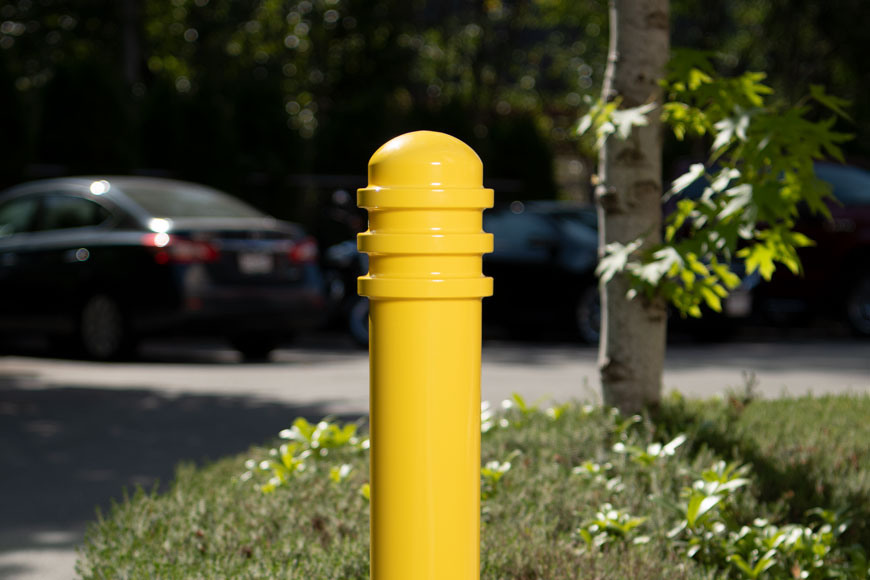
Simple bolt-down bollards are the most cost-effective and are easy to install. They help alert vehicles to potential hazards and ensure optimal flow in designated areas. Bolt-down bollards delineate areas for shopping carts, strollers and wheelchairs if necessary.
Bolt-down bollards are not designed to withstand vehicle impact, and so work best as visual guidance. They are semi-permanent structures. Although they can be removed and relocated without much trouble, they are not meant to be moved on a regular basis, like access control bollards might be.
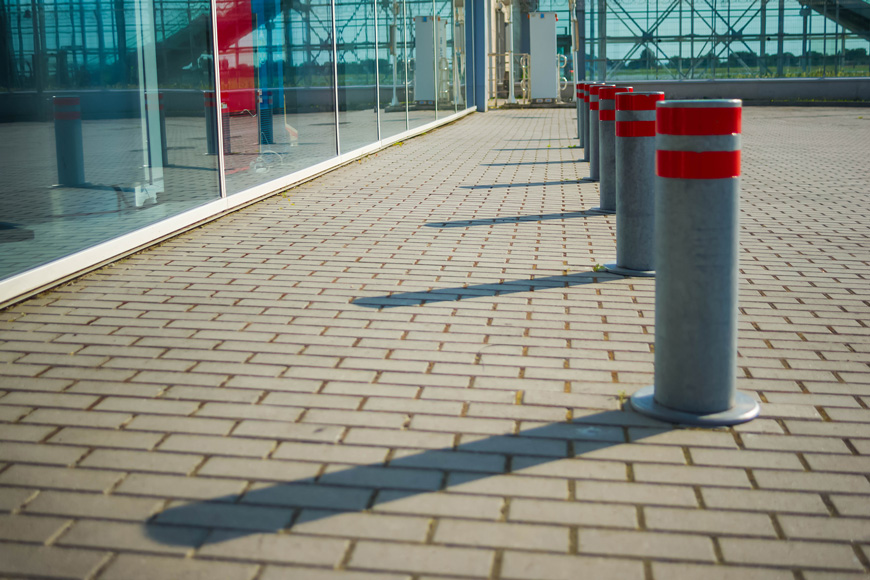
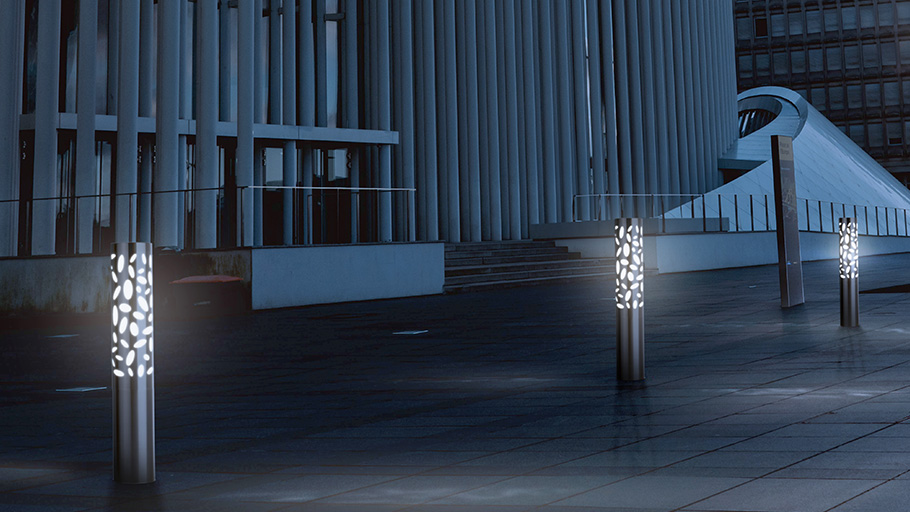
For areas that don’t require impact protection but do need to handle the brush or bump of cars, flexible bollards can be used for visual protection. These polyurethane flexible bollards bend up to 90 degrees when struck, preventing damage to ground surfaces and vehicles. They will return to their upright position and resist damage with repeated impacts—minimizing the need for maintenance, repair and replacement in any parking area.
Physical protection
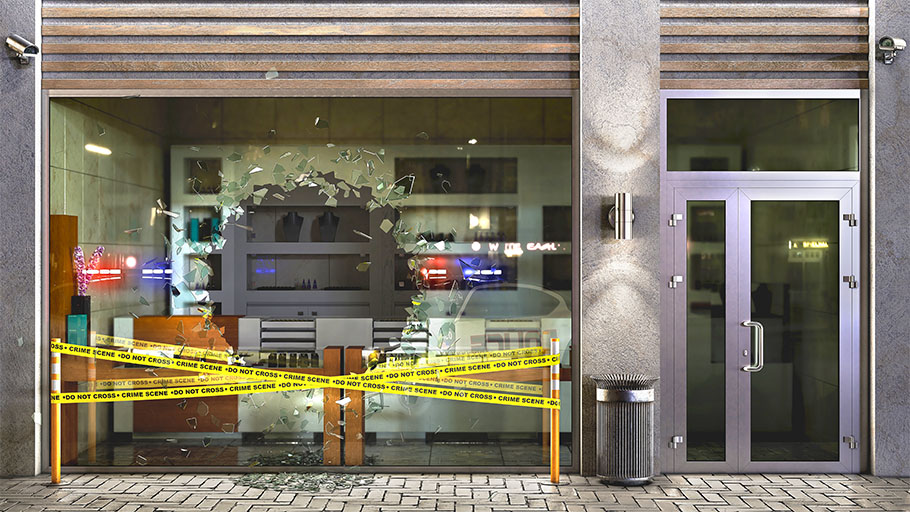
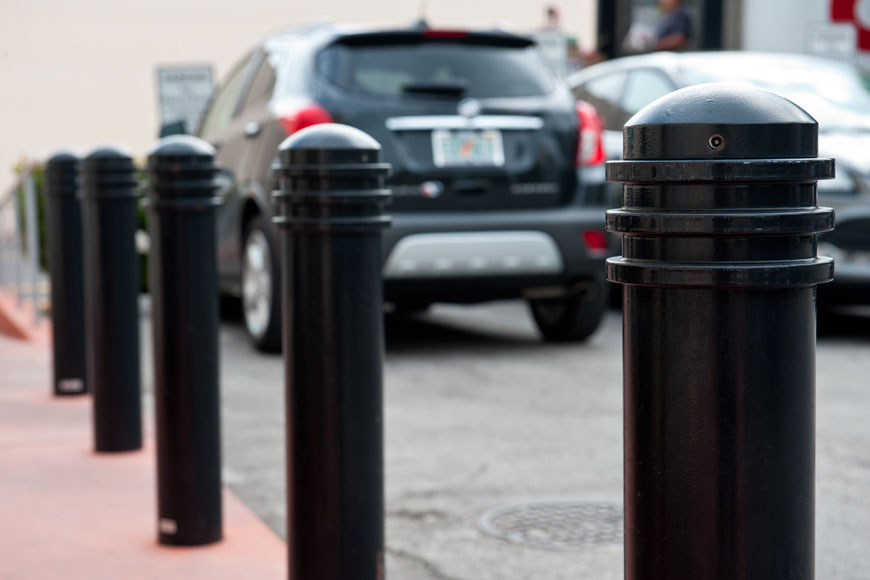
Bollards can provide a strong physical barrier to prevent vehicles from entering restricted areas. Steel pipe bollards offer the most basic form of this physical protection. Made from structural-grade steel, they are embedded deep in concrete to withstand significant shocks. Steel pipe bollards protect not only against vehicle accidents but also against smash-and-grab intrusion. However, their stopping power is variable, and based on local ground conditions and installation. For engineering peace of mind, crash-rated bollards are also available. These have passed standardized tests to prove they stop a vehicle at a specific speed when installed as directed. Both types of high-impact posts are often used to protect building entrances and storefront windows, which can be prime locations for vehicle invasions. Read more about planning perimeter security.
Children, seniors and people in wheelchairs are especially vulnerable in parking lots
The disadvantage of steel pipe bollards is that they aren’t attractive on their own—and without proper care will rust easily. At the very least, steel pipe bollards should be painted regularly to maintain appearances and to prevent corrosion. Installing bollard covers is another alternative to painting, and can be a means to achieving a range of aesthetic styles and designs to complement surrounding architecture and landscapes.
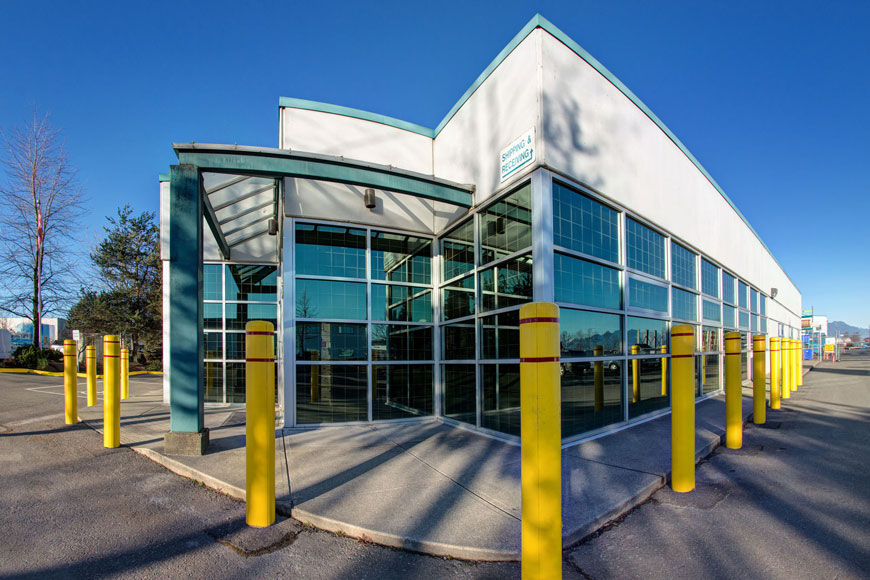

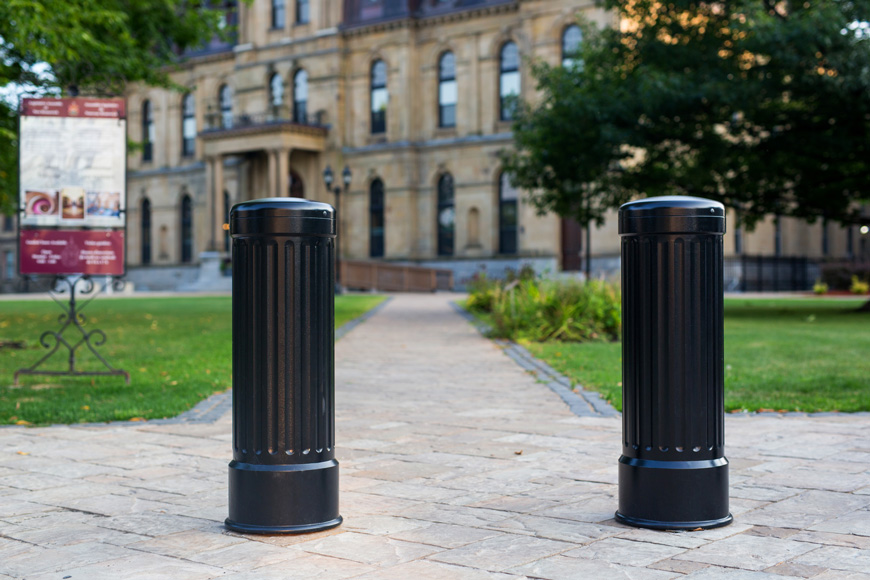
Protective covers and sleeves
Post covers protect steel pipe bollards from rust and damage. They establish better visibility for drivers and pedestrians—and are available in a range of materials, colors and designs to suit any building or landscape. Many covers can also be used on their own as decorative bollards or as visible barriers.
- Plastic covers offer the most basic and economical means for protecting steel pipe bollards—while enhancing visibility in high-traffic areas. Many plastic covers come with reflective strips to heighten prominence.
- Stainless steel covers offer a clean and bright finish that will complement any modern building design. Stainless steel is naturally resistant to corrosion, meaning bollards will always look their best.
- Decorative covers offer the greatest range of premium aesthetics and design, suitable for higher-end buildings and landscapes. Decorative covers can also be used on their own to enhance existing architectural designs. Made from high-quality, powder-coated ductile iron, steel or aluminum, they provide exceptional strength and durability in most North American environments.
Controlling access
Specialized bollards are ideal for controlling access to restricted areas or for customizing spaces for seasonal or day-to-day use. They can be effective for reserved parking areas or areas that require only occasional access by service vehicles. When in place, bollards provide clear, visible guidance to traffic and pedestrians. When removed, they allow temporary vehicle access. Removable bollards can also be detached and stored in the event of a parking lot event.
- Removable bollards are available with a range of embedded mounting options. Bollards can be removed entirely from their receivers to prevent tripping or obstruction.
- Fold-down bollards are ideal for quick vehicle access and require no additional storage when lowered.
- Retractable bollards can be manually lowered into an embedded receiver, creating a clean surface without any additional storage requirements.
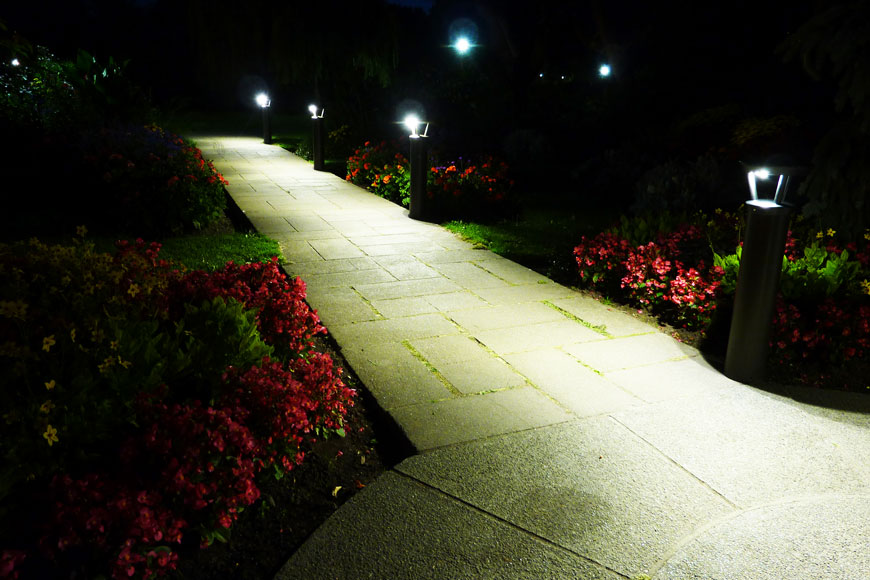

Lighting
Lighting in parking lots can be a big issue for planners. When it comes to planning bollard installations, solar lighting bollards can help ensure visibility for walkways near or surrounding traffic and parking areas—making for safer environments at night and in low-light conditions. Solar lighting units in particular are fully self-contained, meaning no additional trenching or conduits are required.
Accessibility and vulnerable populations
Children, seniors and people in wheelchairs are especially vulnerable in parking lots. Not only can they be less mobile, they can also be less aware—and less visible to drivers. Schools, playgrounds, seniors’ homes, hospitals, and other care centers are especially prime locations for effective parking lot planning.
Quality bollards
Buildings and landscapes should be designed not just for decoration and functionality, but also for long-term use with minimal maintenance. Quality bollards and other site furnishings should be made from top-quality materials to ensure minimal wear and corrosion—to keep bollards looking their best for years to come.