Keep industrial steel wheels in their best working condition

Flanged track wheels are used to transfer heavy loads in industries such as forestry, wood processing, mining, and manufacturing. Buying and maintaining wheels are major expenses in any transfer cart operation. Buying the right type of wheel for the job is essential—a higher quality wheel will pay off with its extended service life and decreased chance of early failure. The service life of industrial wheels can be further extended by following best practices in operation and maintenance.
Follow our tips to get the best value for your wheels.
1. Select the right wheel for the application
The first—and most important step—is in selecting the right cart wheel for the application. A steel wheel should facilitate controlled, efficient movement of heavy duty machinery. Mismatched wheels have the opposite effect, risking failure that can damage operating equipment or pose a safety hazard. Industrial wheels of the wrong composition or size lead to work slowdowns and safety risks. Whether purchasing standard, customized, or fully custom wheels, keep in mind the wheel’s final application and function.

2. Select the best material for your wheel
A suitable material for an industrial wheel is based on the application’s environmental and operating condition. Steel wheels provide decent rust and corrosion resistance, but may not be appropriate for consistently damp or salty environments. In more extreme applications, stainless steel wheels or custom galvanized wheels will be required. Within those broad categories, there are many grades with varying levels of hardness and corrosion resistance.
If the wheel application will be operating in high temperatures, there are select metal grades that fare better in high-temperature environments. Such environments have specific requirements, and it is best to consult an engineer.
3. Handle track wheels with care
Track wheels should always be handled and stored with care. Any scrapes or notches that damage the wheel’s surface interfere with corrosion protection and lead to decreased service life. Once a wheel begins to rust, it requires intensive maintenance or will need to be replaced altogether. Prevention is the best approach for preserving the integrity of the wheel.
4. Adhere to safe working loads
Exceeding load limitations is extremely unsafe and destructive to steel cart wheels. Whether single- or double-flanged, cart wheels can flatten with excessive loads. An over-loaded cart runs the risk of breaking the wheel’s flanges causing significant damage to the track. In order to prevent the dangers of over-loading, be sure to check the industrial wheel’s safe working load, and compare it to the manufacturer’s limitations. A poorly planned wheel assembly is a hazard with the potential to harm operators and bystanders, as well as force operations to shut down.

5. Adhere to speed limits
Steel or iron, flanged or flat-faced—any type of cart wheel is compromised when operating at speeds that exceed suggested speed limits. In addition to being dangerous, excessive speeds will shorten the service life of the wheel by exasperating wear and tear.
6. Keep tracks aligned and level
Tracks are just as integral for wheel operation as the wheels themselves. Misaligned tracks create issues such as side-loading that cause damage to the flanges, and shear-loading that cause damage to the material being transported. The rail joints also require special attention as faulty joints can present problems for flanged wheels.
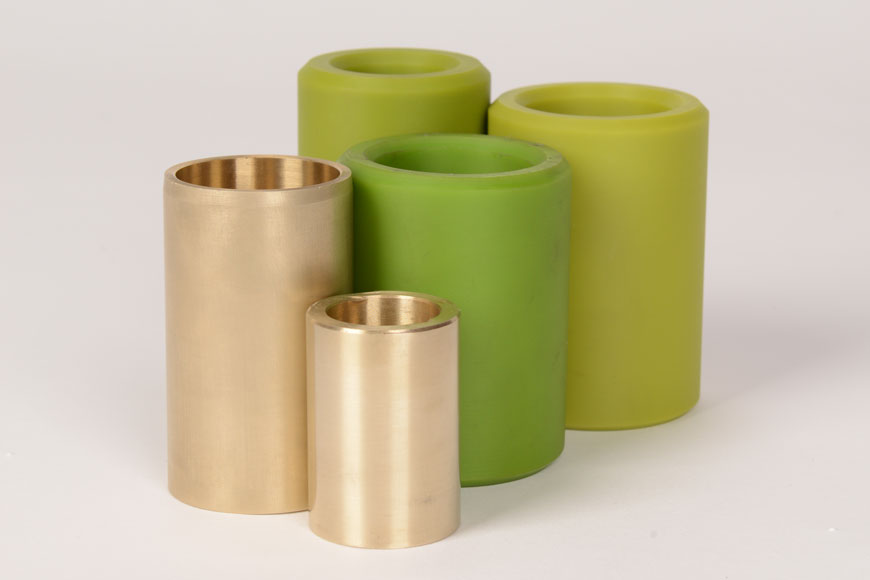
7. Select the right bearing or bushing
Bearings and bushings minimize the friction between a wheel and axle by using a rolling or sliding mechanism. They help to reduce material degradation and prolong the lifespan of industrial wheels. There are a variety of sizes and materials to choose from to suit each application. Bearings are typically more suitable for heavy-duty wheels with higher velocities and lighter loads. Bushings are best for heavier loads at slower speeds.

8. Ensure consistent lubrication
Lubrication is used on bearing and bushing surfaces where they meet the axel. Lubrication can be in the form of grease, oil, or water. It is important to be aware of the lubrication period that suits your wheel application. Regular maintenance will help to ensure that lubrication is always present. Furthermore, the operating environment will also make a difference. Wheels that operate in hot conditions will require lubrication with a high heat tolerance.
9. Inspect and maintain cart wheels
Maintaining industrial wheels is crucial to ensure safe and reliable operation, particularly in applications with shock-loading. Effective maintenance involves regular monitoring, diagnostics, adjustment, and repair. Some key aspects to consider include:
- Flange Tip Wear: Monitor the wear of the flange tip to prevent performance issues.
- Radial Cracking: Watch out for any signs of radial cracking, as it can compromise the wheel’s structural integrity.
- Spalling on Tread Surface: Inspect for spalling on the tread surface, which can affect traction and stability.
- Scaled Wheels: Address scaling on wheels promptly, as it can lead to reduced performance and premature wear.
- Notching: Check for notching, as it can impact the smooth movement of the industrial wheels.
- Pitting: Be vigilant for severe pitting, as it may render the wheels unsafe for use.
If industrial wheels display severe cracking, significant pitting, or notching, it is crucial to remove them from service immediately. However, wheels with less severe damage can often be restored by cleaning or machining them back into working order.
Steel wheels realize a long lifespan when they are suitable for the operating environment, load capacity, and track condition. Bearings and bushings and the right lubrication will also alleviate metal degradation and material wear, making industrial wheel maintenance more manageable.












