Understanding the influences of chemical composition and post-weld heat treatment
The correct material specification of a casting must be identified before placing an order with a foundry. This ensures the desired casting will have the necessary qualities for best performance and durability. Orders for castings at a foundry are typically made to ASTM specifications—a system of classifying steel and other materials based on mechanical properties, chemical analysis, and intended use. ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), is a globally recognized standards organization.

What is ASTM A27?
Depending on the mechanical and chemical properties required, steel (Fe) will contain varying amounts of foreign elements (alloys) in addition to carbon (C). ASTM A27 is a specification developed for carbon steel castings for general applications. Often referred to as mild steel, or plain carbon steel, the balance of cost vs. strength of this common form of cast steel makes it desirable for a wide range of uses.
ASTM A27 provides several grades and two classes of steel castings that can be specified depending on the chemical and strength requirements of the design. It also provides supplementary requirements if castings call for unique inspections and adherence to other design needs. ASTM A27 includes carbon steel castings for applications requiring up to 70 ksi (485 MPa) minimum tensile strength.
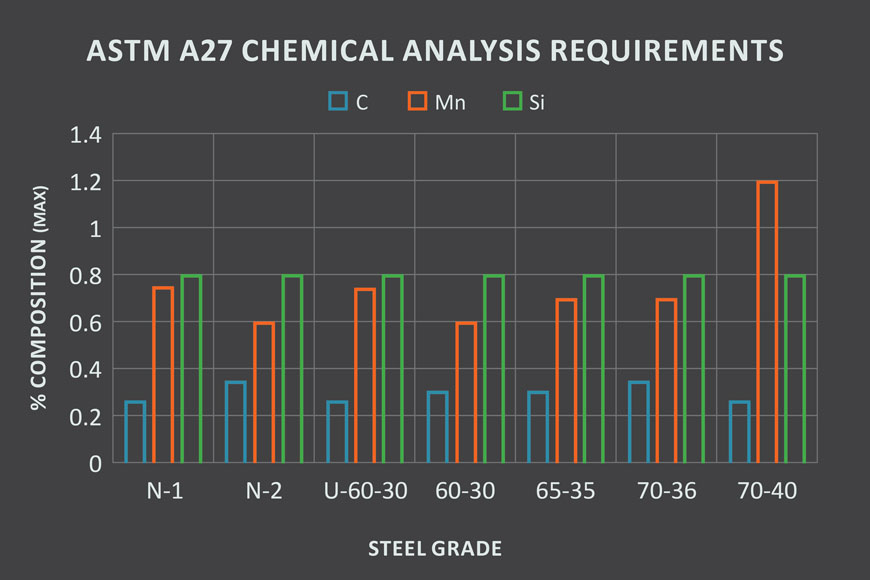
There are several steel grades and two classes of steel castings covered under ASTM A27. Each grade varies based on the chemical composition and type of heat treating needed to affect changes in mechanical properties.
Supplemental tests can be applied to specifications when testing beyond chemical and tensile analyses. Supplemental testing requires producers to conduct from a selection of additional tests.
Effects of heat treatment
Heat treatment is used to alter, repair, or improve the physical properties of metal. This process in a foundry involves heating and chilling using heat-treat ovens, often to extreme temperatures. This reduces stress in a cast part, homogenizes the physical properties of the casting, and modifies the physical properties of the metal. Heat treating involves full annealing, normalizing, and tempering—or quenching and tempering. Heat treatments should be performed after castings have fully cooled.
When considering steel grades and classes, heat treatment plays a crucial role. All castings, with the exceptions of Grade N-1 and U-60-30, must be heat treated. Steel class is largely influenced by the casting’s need for post-weld heat treating.
Selecting a steel grade
When choosing a steel grade, choose one that fulfills actual requirements, rather than a grade that aims to fulfill conditions that are never expected. Higher grades and additional tests will typically demand higher costs. When superfluous testing or acceptance criteria beyond what is needed is performed, expenses are added without necessarily increasing the serviceability of the casting. The amount of testing demanded and the acceptance criteria should follow design and service requirements.
STEEL GRADES
Grade N-1
Chemical analysis only
Grade N-2
Heat treated but not mechanically tested
Grade U-60-30
Mechanically tested but not heat treated
Grade 60-30, 65-35, 70-36 and 70-40
Heat treated but not mechanically tested
Selecting a steel class
After deciding on a steel grade, it is time to choose a steel class. There are two separate classes of steel differentiated by the need for heat treatment.
- Class 1: Post-weld heat treatment required
The foundry must heat treat, or re-heat treat, a casting if any welding is performed. - Class 2: Post-weld heat treatment not required
The foundry may conduct some welding on a casting without necessitating heat treating or re-heat treating. This is normal in the case of very small, cosmetic welds.
If welds require heat treating, it is important to specify Class 1, along with the grade. Contrastingly, if heat treatment will not be used, Class 2 should be specified along with the grade.

ASTM A27 strength testing
Strength tests are typically performed on representative steel bars, called coupons, rather than sections taken from actual castings. Tests made on coupons have the same composition of the casting as they are poured and heat treated at the same time as the castings. The results will show the steel’s quality, but not necessarily the properties of the actual casting. During heat treatment, solidification conditions and cooling rate are affected by the size, shape, and thickness of the casting.
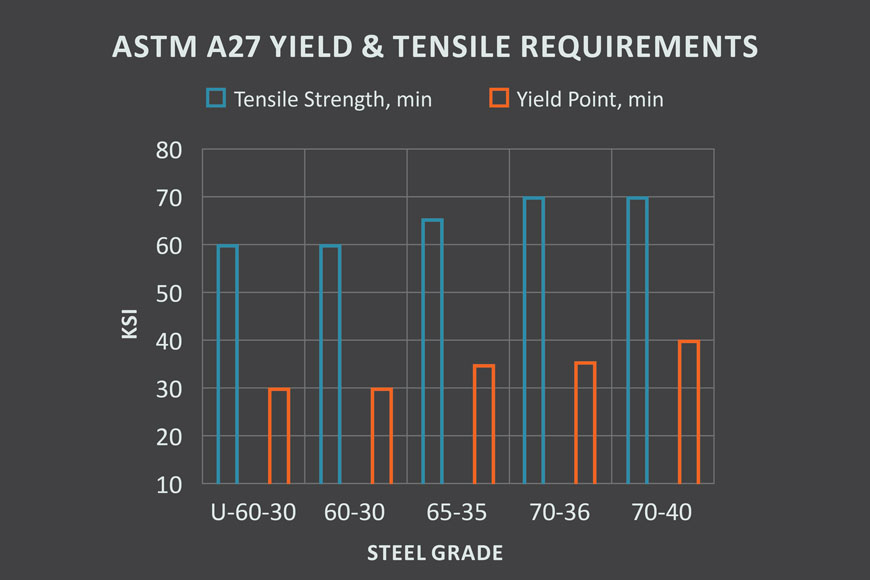
Steel specifications generally refer to the tensile and yield strength. A27 steel, except for Grades N-1 and N-2, must all undergo a tension test and conform to the following mechanical requirements:
Tensile strength (Ultimate tensile strength)
The strength of a material measured by the greatest stress it can undergo while being stretched before breaking.
Yield point
The tension a material can undergo before it starts to deform plastically.
Elongation (%)
The percentage of the initial length that a tensile test piece stretches before breaking or fracturing.
Reduction of area (%)
The difference between the original cross-sectional area of a tensile specimen and the smallest area after rupture (expressed as a percentage of the original area).
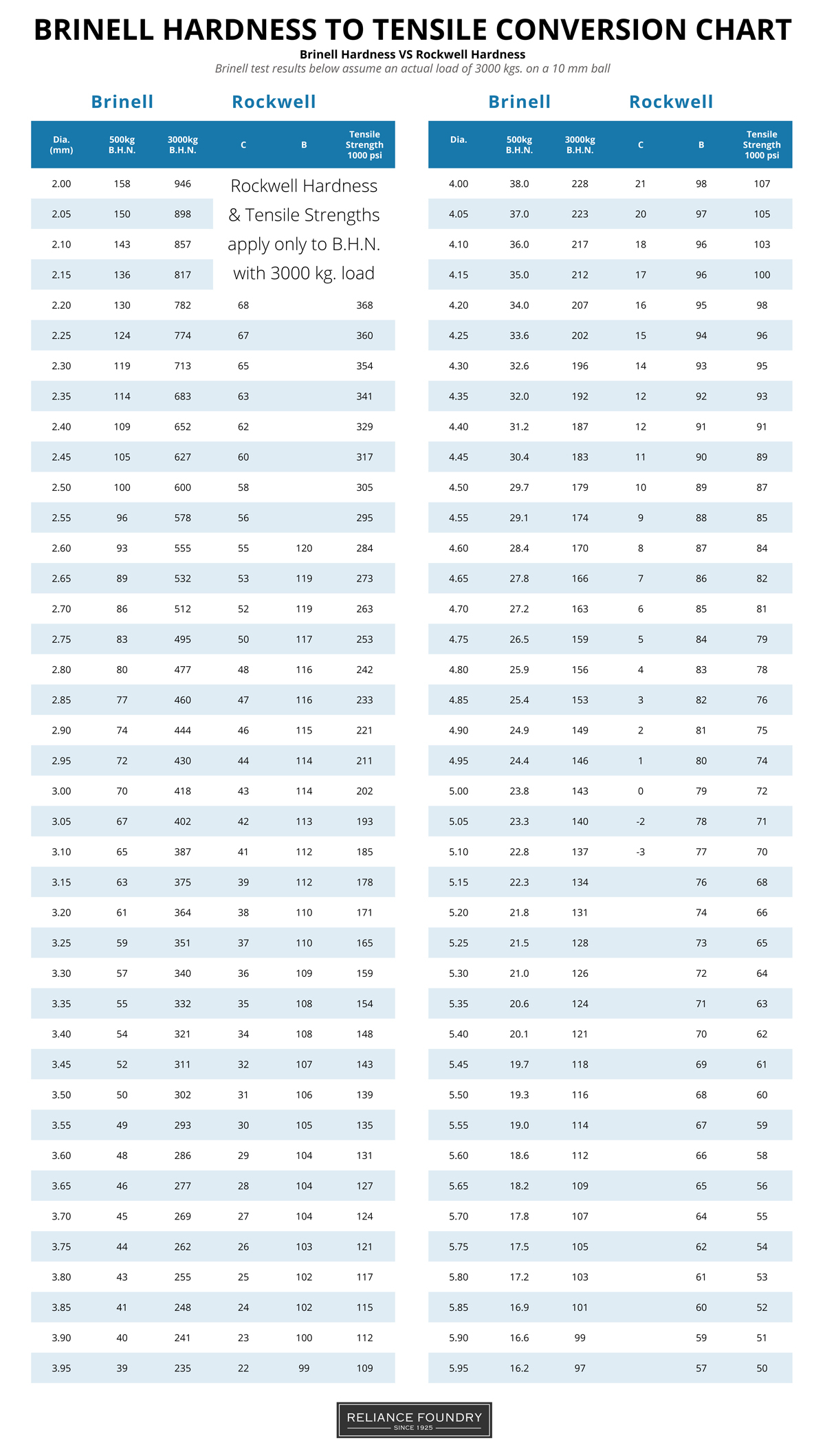
Strength tests vs. hardness tests
Tensile strength is not the same as hardness. Tensile strength refers to the resistance of a material to breaking under tension. As mentioned earlier, tensile strength can be tested using test coupons to verify tensile properties including tensile strength, yield point, and elongation of the casting.
Hardness refers to the ability for a material to resist deformation. When it comes to non-austenitic steel, there is a consistent functional relationship between hardness values and tensile strengths, and therefore measuring hardness can indicate tensile yields. In the foundry hardness testing provides a cheap, easy, and systematic way of checking for physical properties without having to perform unique tensile tests. Although they do not provide an exact or guaranteed measurement, they are relatively accurate for homogenous steels. Therefore, hardness testing and subsequent conversion can provide a rapid, cost-effective method of quickly confirming physical property assumptions.